Teeth Alignment: A Comprehensive Guide
Table of Contents
Teeth Alignment: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
Achieving a beautifully aligned smile enhances oral health and well-being. Teeth alignment, or occlusion, refers to how upper and lower teeth fit together when the mouth is closed. Proper alignment ensures optimal function, reduces dental issues, and improves quality of life. This guide explores the importance of teeth alignment, treatment methods, benefits, risks, costs, and duration.
Understanding Teeth Alignment
Teeth alignment, a focus of orthodontics, diagnoses and treats “bad bites” (malocclusion) and straightens teeth to improve aesthetics, function, and oral health.
What is Teeth Alignment?
Teeth alignment positions teeth relative to each other and the jaws for a perfect bite and functionality, ensuring even distribution of biting forces.
Teeth Alignment vs. Teeth Straightening
Teeth straightening focuses on the cosmetic aspect of moving crooked teeth, often the front ones. Teeth alignment is broader, addressing functional issues like overbites, underbites, crossbites, spacing, and jaw alignment for a healthy bite.
The Ideal Bite
An ideal bite has upper teeth slightly overlapping lower teeth, with upper molar cusps fitting into lower molar grooves. The midline of upper and lower front teeth aligns with the face’s center, with teeth straight vertically and horizontally, without significant crowding or gaps.
Causes of Misaligned Teeth (Malocclusion)
Malocclusion stems from various factors:
Genetic Predisposition
Hereditary factors influence jaw size and shape, causing crowding, extra teeth, overbites, underbites, or developmental issues. Smaller modern jaws often lead to crowding.
Poor Myofunctional Habits
Childhood habits like prolonged thumb sucking, tongue thrusting, mouth breathing, or nail-biting can misalign teeth or affect jaw development.
Poor Dental Care and Nutrition
Neglecting dental check-ups or poor nutrition can lead to decay, tooth loss, or impaired dental development, causing misalignment.
Injury, Trauma, and Other Factors
Facial trauma, early loss of baby teeth, ill-fitting restorations, impacted teeth, TMJ disorders, or gum disease can contribute to misalignment.
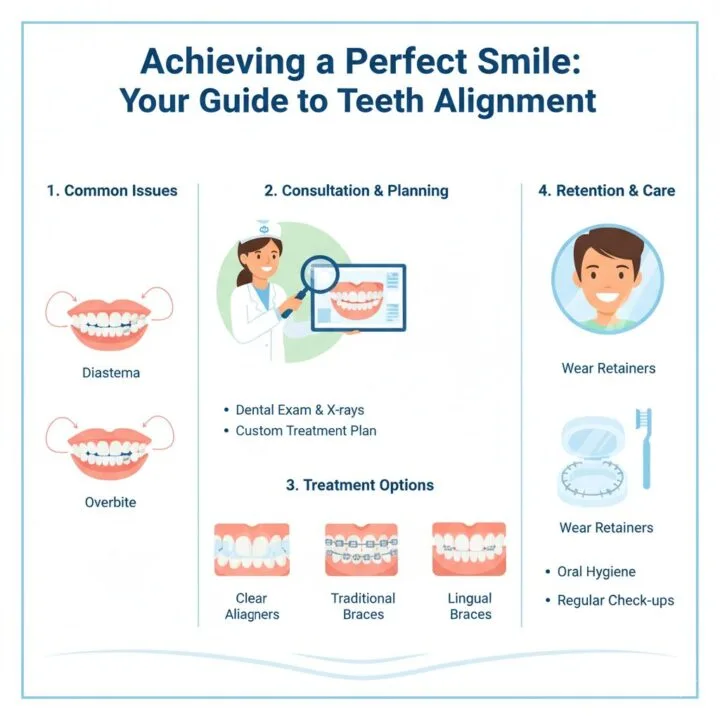
Types of Malocclusion
Malocclusion types include:
- Class I Malocclusion: Proper molar alignment with minor front teeth crowding or spacing.
- Class II Malocclusion (Overbite): Upper teeth/jaw protrude significantly, risking tooth wear and jaw pain.
- Class III Malocclusion (Underbite): Lower teeth/jaw protrude, affecting chewing and speech.
- Crossbite: Upper teeth fit inside lower teeth, causing uneven wear or gum recession.
- Diastema: Noticeable gaps between teeth, often cosmetic.
- Open Bite: Front teeth don’t touch when closed, impacting biting and speech.
Benefits of Proper Teeth Alignment
Improved Oral Hygiene
Straight teeth are easier to clean, reducing risks of cavities, gingivitis, and periodontitis.
Better Chewing and Digestion
Proper alignment ensures efficient chewing, aiding digestion and nutrient absorption.
Reduced Tooth Damage and Pain
Alignment prevents uneven wear, chipping, fractures, and TMJ-related issues like jaw pain or headaches.
Enhanced Overall Health
Proper alignment improves speech, reduces gum disease linked to systemic issues (e.g., heart disease), and may enhance breathing. It also boosts self-esteem and confidence.
Methods of Teeth Alignment
Orthodontic treatments vary by need and preference:
Traditional Metal Braces
- Effectiveness: Highly effective for complex cases.
- Visibility: Noticeable.
- Cost: $2,750–$7,500.
- Duration: 18–36 months.
Ceramic Braces
- Aesthetics: Less noticeable with tooth-colored materials.
- Cost: $2,000–$8,500.
- Duration: 12–36 months.
Lingual Braces
- Discretion: Placed on teeth’s back, nearly invisible.
- Cost: $5,000–$15,000.
- Duration: 12–36 months.
Self-Ligating Braces
- Efficiency: Uses clips, reducing friction and appointments.
- Cost: $2,000–$8,500.
- Duration: 12–30 months.
Clear Aligners (e.g., Invisalign)
- Discretion: Nearly invisible, removable trays.
- Suitability: Best for mild to moderate issues.
- Cost: $1,800–$9,500.
- Duration: 6–24 months.
Dental Surgery
- Effectiveness: Corrects severe jaw issues with braces.
- Complexity: Significant intervention.
Retainers
- Purpose: Maintains alignment post-treatment.
Cosmetic Dentistry
- Veneers/Bonding: Improves appearance for minor issues without moving teeth.
Duration and Cost Considerations
Treatment Duration
- Severity: Complex cases take longer.
- Type: Braces (18–36 months), aligners (6–24 months).
- Age: Younger patients (10–14) often see faster results.
- Compliance: Adhering to instructions shortens duration.
Cost Factors
- Complexity: Severe cases cost more.
- Appliance: Aesthetic options are pricier.
- Location/Expertise: Varies by region and orthodontist.
- Insurance: May reduce costs; check coverage.
Risks and Complications
Common Discomforts
- Soreness: Temporary after adjustments.
- Irritation: Braces may irritate cheeks or lips.
- Speech Issues: Temporary with lingual braces or aligners.
Oral Hygiene Challenges
- Plaque Buildup: Increases cavity and gum disease risk.
- Discoloration: Poor hygiene may cause staining.
- Gum Recession: Pressure may affect gums.
Dental and Jaw Issues
- Root Resorption: Rare root shortening.
- TMJ Disorders: Possible discomfort during treatment.
- Tooth Vitality Loss: Rare, may require root canal.
Relapse and Allergies
- Relapse: Teeth may shift without retainers.
- Allergies: Rare reactions to brace/aligner materials.
Recent Innovations
Guidelines
The American Association of Orthodontists emphasizes consulting qualified orthodontists, holistic care, and post-treatment retainers.
Innovations
- Advanced Aligners: Improved materials and comfort.
- AI/Smart Tech: Enhances planning and remote monitoring.
- Accelerated Orthodontics: Techniques like micro-osteoperforations or laser therapy speed up treatment.
- Digital Scanning/3D Printing: Creates precise appliances.
- Eco-Friendly Materials: Sustainable aligner production.
- Teleorthodontics: Remote monitoring via apps.
Scientific Studies
- Fixed appliances improve occlusal outcomes.
- Extraction treatments may yield better results in some cases.
- Aligners match braces’ effectiveness for many issues.
- Accelerated methods show promise but vary in evidence.
Conclusion
Proper teeth alignment enhances oral hygiene, chewing, speech, systemic health, and confidence. With options like braces, aligners, and surgery, tailored treatments meet diverse needs. Despite potential discomfort and costs, advancements in orthodontics ensure efficient, personalized solutions. Consult a qualified orthodontist to start your journey to a healthier, confident smile.
FAQ
Q1: Ideal age for treatment?
Best between 10–14, but effective at any age with healthy gums and bone.
Q2: Treatment duration?
Braces: 18–36 months; aligners: 6–24 months. Compliance is key.
Q3: Benefits beyond aesthetics?
Improves hygiene, chewing, speech, and systemic health while reducing tooth damage.
Q4: Are aligners as effective as braces?
Yes, for mild to moderate issues; severe cases may need braces or surgery.
Q5: Will teeth shift back?
Yes, without retainers, relapse is likely. Follow orthodontist’s instructions.
Citations
- – American Association of Orthodontists (AAO) – aaoinfo.org
- – University of Illinois Chicago College of Dentistry – uic.edu








Post Comment